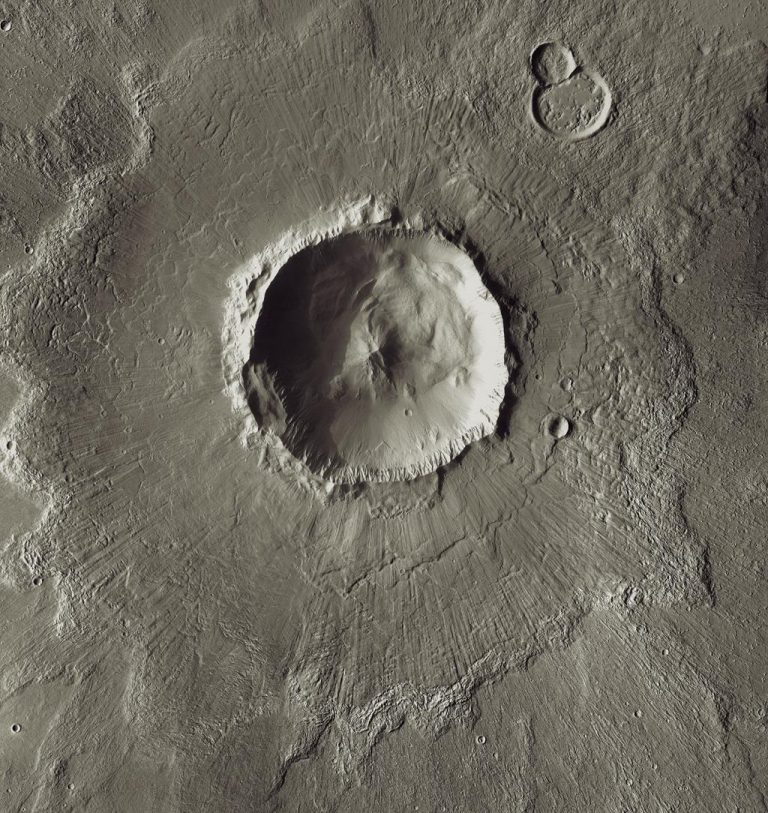
Contact and Compression Stage
When a hypervelocity impact occurs, the impactor compresses sending out a shock wave into the surrounding rocks. The shock waves also pass through the impactor itself, and as the wave passes through it causes the impactor to undergo a significant amount of pressure. When the shock wave reaches the upper surface of the projectile, it is reflected back as a tensional wave or rarefaction wave. It is this reflect wave that releases or unloads the built up pressure from the shockwave. The release of pressure results in a rapid release of energy that melts or vapourizes the projectile.
A similar process occurs within the surrounding. As the shock wave passes through, it induces a huge amount of pressure onto the rocks. As the shock wave interacts with the surface, a rarefaction wave is reflected down into the ground. Like in the case of the projectile, it is the build-up of pressure by the shock wave, followed by the release of the pressure by the rarefaction wave that transforms the surrounding rocks. The point at which the projectile is unloaded is generally taken to be the end of the contact and compression stage.
Excavation Stage
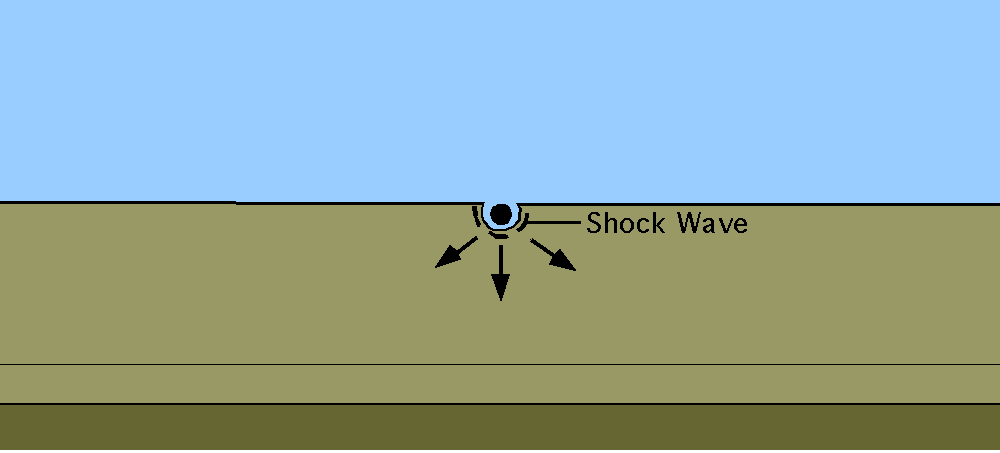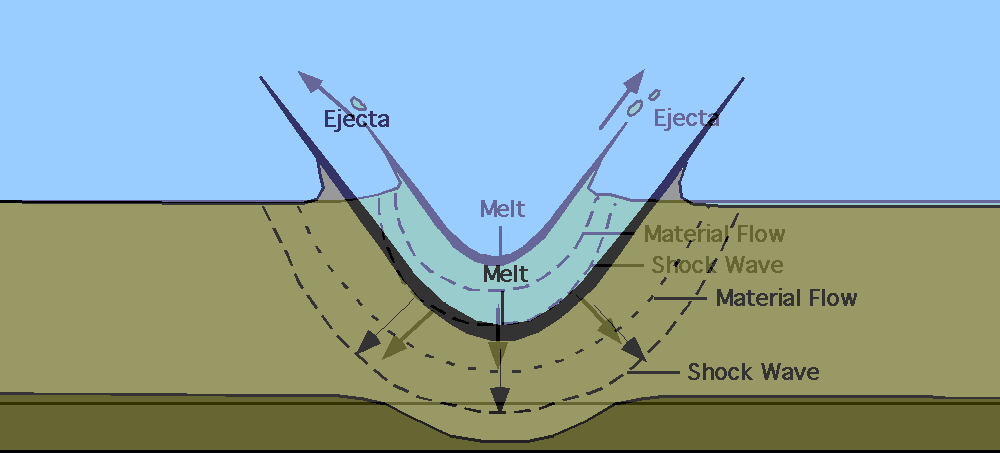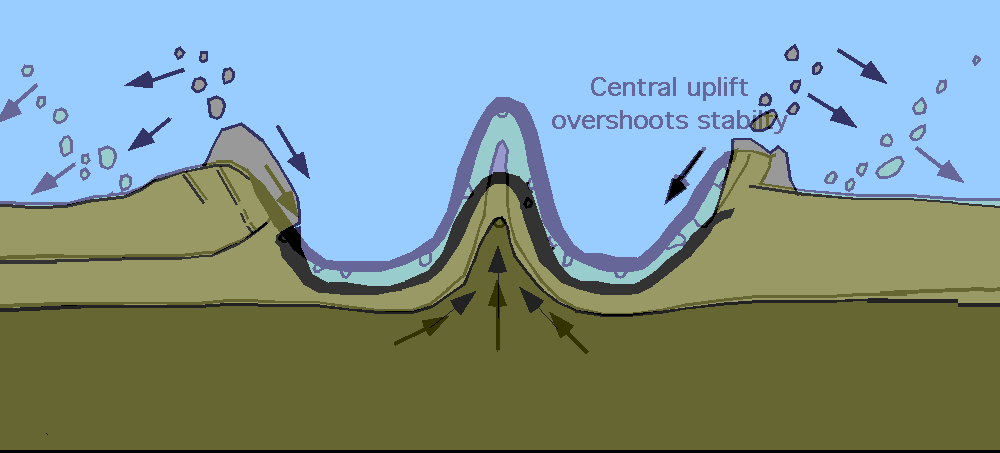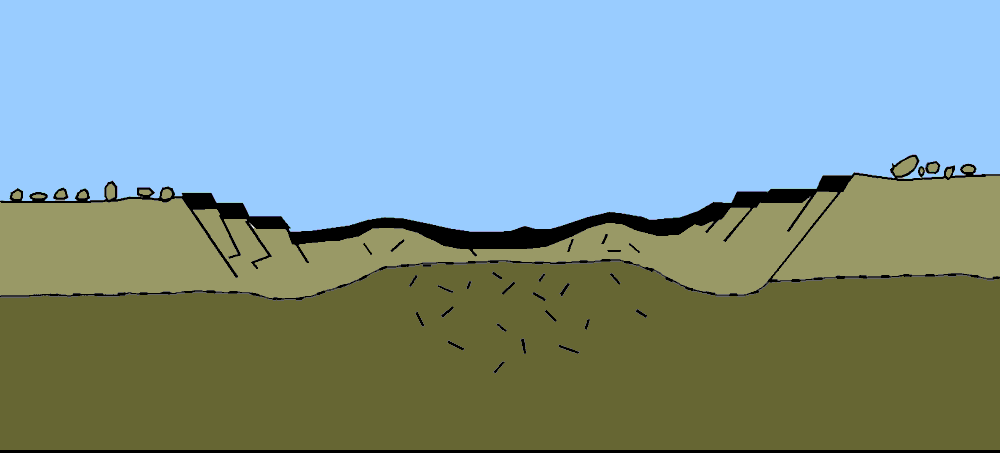
In the excavation stage, the kinetic energy transmitted to the target rocks by the shock wave and rarefaction waves create particle trajectories defining an excavation flow-field. A conceptual transient cavity is created by the physical compression and excavation flow-field of the target rocks. The different trajectories of target rocks result in the division of the transient cavity into an upper excavated zone and lower displaced zone. The excavated zone, made up of fragmented rocks and portions of impact melt, is ejected beyond the transient cavity creating an impact ejecta blanket. The melt and fragmented rock in the displaced zone is shot outwards, but without enough kinetic energy to be ejected from the cavity. This material remains inside the crater into the modification stage. The excavation stage ends at the point in time when motion caused by the shock and rarefaction waves can no longer displace target rocks.
Modification Stage
The final morphology of the crater depends heavily on the size of the crater. Smaller, simple craters undergo little change and remain bowl-shaped; however, larger complex craters (>4 km on Earth) undergo significant change. Modification in a complex impact crater begins when gravitational force cause instability in the transient cavity. Uplift begins in the centre of the cavity as the material moves inwards and upwards forming a central uplift. The steep walls of the rim begin to collapse inwards causing the crater to “flatten” in appearance.
The modification stage of the impact cratering process is thought to begin when the transient cavity is excavated; however, the modification stage has no end. Once the walls collapse and the uplifting ceases erosion begins. On Earth, erosion and plate tectonics continues to alter the final morphology of the crater.
